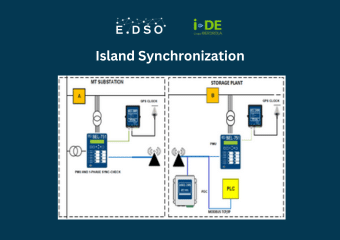
Gensets are commonly deployed to ensure the continuity of power supply in the event of disconnection due to incidents or during maintenance work on the distribution grid. However, conventional generators present several drawbacks: their CO2 emissions, the emission of noise pollution and unpleasant odours. For this reason, Enedis decided to investigate alternative environmentally friendly solutions including several Lithium-Ion (Li-Ion) battery-based generators.
These battery-based generators are able to provide a temporary power supply to customers who are connected to an islanded part of the electricity grid and are able to disconnect or connect renewable sources by managing frequency according to the needs of the islanded network. Today, Enedis operates twelve Li-Ion battery generators and is working on a roadmap for the full replacement of its conventional generators.